Solution for skin necrosis and exposed tendon of the dorsum of the foot
Key Clinical Message
For the treatment of skin necrosis with exposed tendons in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) foot, we should perform microvascular free flap surgery at an early stage without conservative treatment considering the increased risk of infection and the decreased physical activity.
Keywords: dorsum of the foot, foot necrosis, friable skin, microvascular flap, treatment failure
1. INTRODUCTION
Delayed wound healing of dorsal foot skin necrosis can be problematic for patients. The aim of wound treatment is to cover the bone and joint, ensuring that the necrosis is fully covered. The tendon should be covered as fully as possible and treated with free tissue transfer. We performed an extensor digitorum brevis (EDB) flap for the skin necrosis in which the primary skin defect was covered, but the patient had a new skin necrosis at the donor site of the local flap. The patient was subsequently treated for donor site skin necrosis via negative‐pressure wound therapy (NPWT). Through several therapeutic failures, we sought to determine the appropriate treatment for dorsal foot skin necrosis with exposed tendon.
2. CASE REPORT
A 78‐year‐old man suffered from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (stage IV, class 2) for about 24 years. He had never undergone surgery on his extremities. He was administered methotrexate (4 mg/wk), oral corticosteroids (4 mg/d), and iguratimod (25 mg/d) and had a high course of disease activity (DAS 28‐ESR 4.63). He had pulmonary emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis, as well as chronic kidney failure. In early 2014, he experienced foot pain while walking (Figure 1A).

Figure 1
Photographs of the foot. A, Preoperative left foot photograph. Patient had been suffering from rheumatoid arthritis for an extended period and had friable skin. B, Three weeks after surgery, the wound shows maceration upon suture removal. The extensor hallucis longus tendon is still exposed after NPWT. C, D, An extensor digitorum brevis flap was grafted. The site where the EHL was exposed was covered with the flap. E, The skin necrosis occurred at the margin of the lateral donor site without exposed tendon. We performed closure via topical negative‐pressure wound therapy. F, Four months after perforator flap inset, the wound had closed
In X‐ray findings, significant deformations of both sides of the great toe were observed (Figure 2A). The patient had an ulcer inside the left metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP). The hallux valgus angle was 52° on the right and 49° on the left. The M1M2 angle was 23° on the right and 18° on the left. The patient required treatment and did not wish to undergo arthrodesis because his job necessitated squatting. Therefore, he had undergone bilateral Swanson implant arthroplasty for the MTP joint of the great toe in October 2014 (Figure 2B).
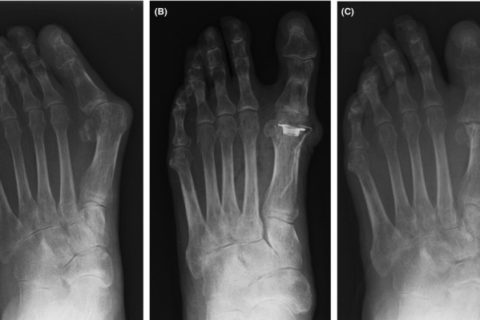
Anteroposterior foot radiographs. A, Patient had pronounced toe deformation. B, After Swanson arthroplasty, deformity of the hallux was corrected. C, At final examination, after removal implant, the hallux metatarsophalangeal joints demonstrated fibrous union
We made a straight incision at the dorsal MTP joint. We expanded the joint capsule to avoid the inward extensor hallucis longus (EHL) tendon. Articular cartilage of the great toe was invaded by synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. We closed the skin without significant problems. The patient began indoor walking with full weight‐bearing 1 week after surgery. All stitches were removed 14 days after surgery. The wound of the right foot presented no issues, but we found that the wound of the left foot was macerated, and the EHL tendon was exposed from the wound site. The wound was 3 × 4 cm in size. NPWT was performed on the wound site on the same day, but the wound did not close. Three weeks later, secondary wound closure was attempted and the implant was removed. We immobilized the MTP joint by K‐wire; however, the EHL tendon remained exposed (Figure 1B). By the end of October 2014 (1 month postsurgery), an extensor digitorum brevis (EDB) flap was used to cover skin necrosis (Figure 1C,D). Bone and exposed tendon were sufficiently covered with this flap. However, new skin necrosis occurred at the margin of the lateral donor site without the exposed extensor (Figure 1E). Topical NPWT was performed, and good granulation was observed for 2 weeks. The patient spent 6 weeks to heal the first skin defect and spent more 4 weeks to treat the donor site necrosis. Throughout the treatment period, no pathogenic bacteria were detected in laboratory cultures. In February 2015, at the final examination, the wound had closed (Figure 1F and and 2C).
Authors
Correspondence Yoichi Toyoshima, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Showa University School of Medicine, 1‐5‐8 Hatanodai, Shinagawa‐ku, Tokyo 142‐8666, Japan (pj.ca.u-awohs.dem@amihsoyot).
Original source
References
| [1] | Bibbo C. Wound healing complications and infection following surgery for rheumatoid arthritis. Foot Ankle Clin. 2007;12(3):509‐524, vii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [2] | Harrison DH, Morgan BD. The instep island flap to resurface plantar defects. Br J Plast Surg. 1981;34(3):315‐318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [3] | Lee SH, An SJ, Kim NR, Kim UJ, Kim JI. Reconstruction of postburn contracture of the forefoot using the anterolateral thigh flap. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(4):444‐451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [4] | Houdek MT, Wagner ER, Pensy RA, Eglseder WA. Extensor digitorum brevis flap for the coverage of ankle and dorsal foot wounds: a technical trick. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(12):e404‐e408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [5] | Llanos S, Danilla S, Barraza C, et al. Effectiveness of negative pressure closure in the integration of split thickness skin grafts: a randomized, double‐masked, controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2006;244(5):700‐705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [6] | Gibstein LA, Abramson DL, Sampson CE, Pribaz JJ. Musculofascial flaps based on the dorsalis pedis vascular pedicle for coverage of the foot and ankle. Ann Plast Surg. 1996;37(2):152‐157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [7] | Hartrampf CR Jr, Scheflan M, Bostwick J 3rd. The flexor digitorum brevis muscle island pedicle flap: a new dimension in heel reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1980;66(2):264‐270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [8] | Torres LR, Paganelli PM, Dos Santos RP, Targa WH, Fernandes TD, Mattar R. Extensor digitorum brevis flap on the treatment of lower limb injuries. Acta Ortop Bras. 2014;22(2):86‐89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [9] | Yoshida A, Yajima H, Murata K, et al. Post‐traumatic big toe reconstruction using free flaps. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006;22(4):255‐260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [10] | Chattar‐Cora D, Pederson WC. Experience with the extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap for foot and ankle reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;57(3):289‐294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [11] | Pai CH, Lin GT, Lin SY, Lin SD, Lai CS. Extensor digitorum brevis rotational muscle flap for lower leg and ankle coverage. J Trauma. 2000;49(6):1012‐1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [12] | Wan‐Chan A, Gingert C, Angst E, Hetzer FH. Clinical relevance and effect of surgical wound classification in appendicitis: retrospective evaluation of wound classification discrepancies between surgeons, Swissnoso‐trained infection control nurse, and histology as well as surgical site infection rates by wound class. J Surg Res. 2017;215:132‐139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [13] | Convertino VA, Bloomfield SA, Greenleaf JE. An overview of the issues: physiological effects of bed rest and restricted physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1997;29(2):187‐190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [14] | Nassar J, Cracchiolo A 3rd. Complications in surgery of the foot and ankle in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;391:140‐152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [15] | Yano K, Ikari K, Ishibashi M, Momohara S. Preventing delayed union after distal shortening oblique osteotomy of metatarsals in the rheumatoid forefoot. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(4):546‐550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |
| [16] | Ishie S, Ito H, Azukizawa M, et al. Delayed wound healing after forefoot surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(3):367‐372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] |