Treatment and restoration of adult dentoalveolar trauma
Abstract
Adult dentoalveolar trauma most often occurs in the context of sports activities and traffic accidents. Coronal fractures are the most common type of lesion, followed by tooth luxation. We present the case of a 25-year-old woman who suffered alveolar bone damage and coronal fractures of the upper incisors, with extrusive luxation of the right central incisor, as the result of a fall. On the first visit, manual reduction of the buccal plate was carried out under local anesthesia, with repositioning of the right central incisor and splinting to the neighboring teeth. Composites were used to restore the coronal fractures. After one month, both upper central incisors and the right lateral incisor were subjected to endodontic treatment. Internal bleaching of the right lateral incisor was also carried out, due to pigmentation secondary to pulp necrosis. At follow-up 5 months later, the alveolar bone fracture was seen to have healed. Definitive anterior restorative treatment with porcelain veneers was therefore carried out. After two years the patient remains asymptomatic and in good dental condition.
Key words:Dental trauma, extrusive luxation, dento-alveolar fracture, esthetic restoration
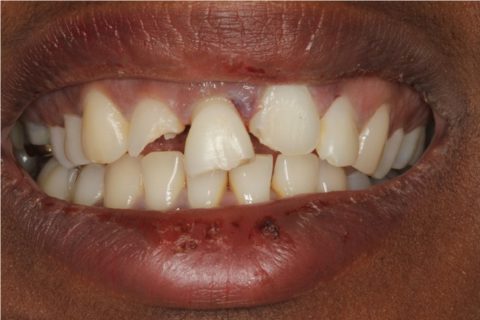
Initial intraoral view showing the coronal fractures of the incisors and extrusive luxation of the upper right central incisor.
Case Report
A healthy 25-year-old woman visited our dental clinic 24 hours after an accidental fall. The physical examination revealed contusion of the lower lip, uncomplicated coronal fracture of all four upper incisors (Fig.1), and extrusive luxation of the upper right central incisor, which was also confirmed by the X-ray study (Fig.2). Alveolar fracture of the upper anterior buccal plate was identified by cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) (Fig. 3)(1,3,4).
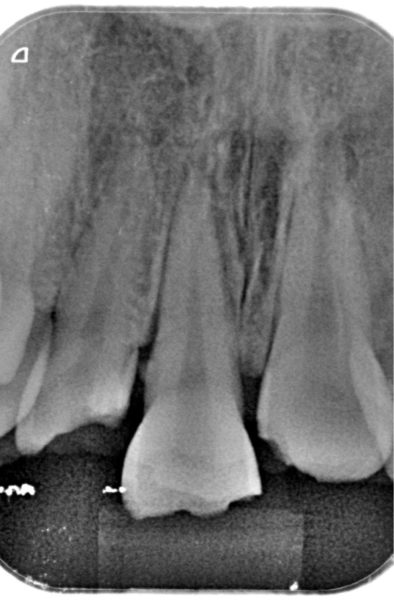
Periapical X-ray view of the upper central incisors, showing widening of the periodontal ligament of the upper right central incisor secondary to extrusive luxation.
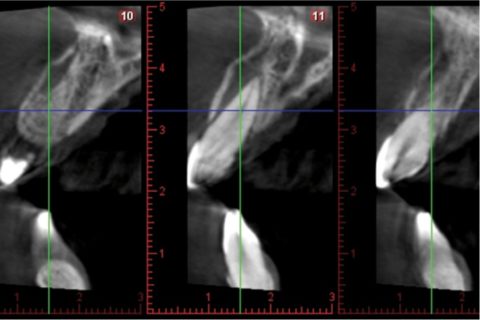
CBCT view showing of the upper central incisors, showing the alveolar fracture of the upper anterior buccal plate.
On the first visit and under local anesthesia, we repositioned the upper right central incisor within its socket, followed by splinting to the neighboring teeth with wire and composite material. Provisional reconstruction of the coronal fractures with composite was also carried out on the same visit. Antibiotic treatment was prescribed in the form of amoxicillin 875 mg and clavulanic acid 125 mg (Augmentine®, GSK,80 G, Brentford, Middlesex, United Kingdom), together with analgesia in the form of ibuprofen 600 mg (Normon, Madrid, Spain), during one week .
Three weeks later vitality testing using a tetrafluoroethane spray (Pharmaethyl®, Septodont, Saint-Maur-des-Fossés, France) yielded negative results with both upper central incisors and the right lateral incisor. Endodontic treatment of these teeth was sub-sequently carried out, with internal bleaching of the upper right lateral incisor using 35% hydrogen peroxide (Opalescence Endo; Ultradent, South Jordan, UT, USA), due to discoloration secondary to pulp necrosis. Internal bleaching lasted four weeks, after which composite veneers were prepared (Filtek Supreme XTE; 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA) for all four upper incisors in order to improve the esthetic outcome (Fig.4).
Provisional composite veneers of the four upper incisors.
Following stabilization of the clinical and esthetic condition of the patient, and after a 5-month waiting period, CBCT evaluation of the alveolar bone fractures confirmed healing of the buccal plate.
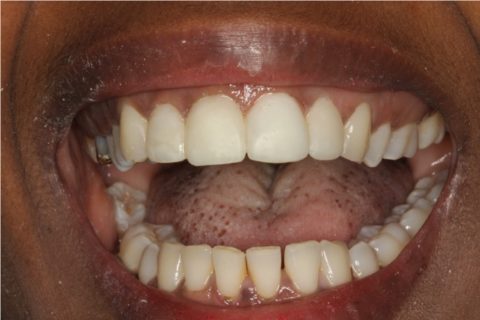
As final restoration, esthetic tests were made for the fitting of lithium disilicate veneers (IPS e.max Press; Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein) on the four upper incisors. Preparation for veneers with a buccal thickness of 0.5 mm and a curved chamfer of 0.3-0.5 mm was carried out (Fig. 5), followed by imprinting with triple-zero retraction thread (Ultrapak; Ultradent, South Jordan, UT, USA) and polyether (Impregum; 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA) as imprint material. The veneers were cemented using an adhesive technique (Variolink Veneer; Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein), and resulted in a more natural smile (Figs. 6,7).
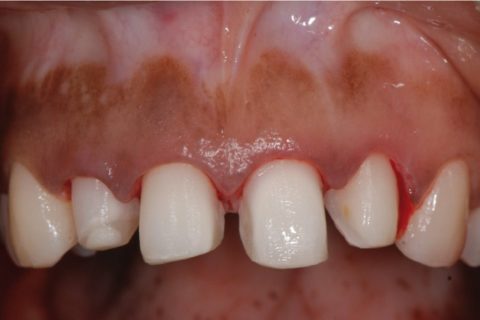
Preparation for veneerson the four upper incisors.
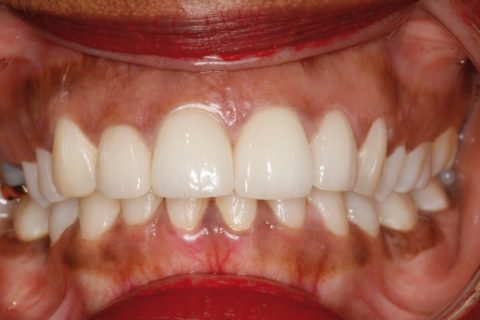
Intraoral view of the porcelain veneers on the upper incisors.
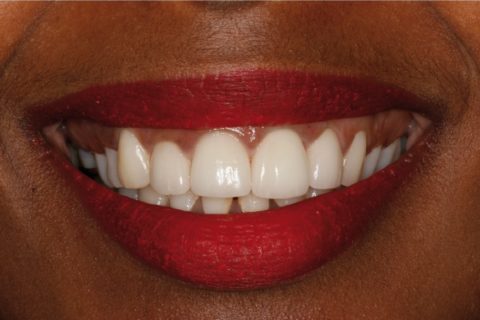
Extraoral view of the porcelain veneers on the upper incisors.
After two years the patient remains asymptomatic, with no signs of root resorption or ankylosis of the damaged teeth.
1Postgraduate student in Prosthodontics. Department of Buccofacial Prostheses. University Complutense of Madrid. Spain
2Chairman of Oral Surgery, Stomatology Department, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Valencia, Spain
3Full Professor of Oral Surgery, Stomatology Department, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Valencia, Spain
4Associate Professor of the Department of Stomatology. Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, Valencia University, Spain
Corresponding author.Clínicas Odontológicas Gascó Oliag 1, 46021 – Valencia, Spain , E-mail: moc.liamg@rotsaparres.acnalbConflict of interest statement:The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Copyright : © 2016 Medicina Oral S.L.
1. Andreasen JO, Lauridsen E, Andreasen FM. Contradictions in the treatment of traumatic dental injuries and ways to proceed in dental trauma research. Dent Traumatol. 2010;26:16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2. Robertson A, Robertson S, Norén JG. A retrospective evaluation of traumatized permanent teeth. Int J Paediatr Dent. 1997;7:217–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
3. Andreasen JO, Andreasen FM, Skeie A, Hjørting-Hansen E, Schwartz O. Effect of treatment delay upon pulp and periodontal healing of traumatic dental injuries –a review article. Dent Traumatol. 2002;18:116–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
4. Andreasen JO, Andreasen FM. Clinical and Radiographic Findings with the Various Luxation Types. In Essentials of Traumatic Injuries to the Teeth: A Step-by-Step Treatment Guide, Second Edition . Oxford : UK: Blackwell Munksgaard ; 2000. [Google Scholar]
5. Yonezawa H, Yanamoto S, Hoshino T, Yamada S, Fujiwara T, Umeda M. Management of maxillary alveolar bone fracture and severely intruded maxillary central incisor: report of a case. Dent Traumatol. 2013;29:416–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
6. Oikarinen K, Andreasen JO, Andreasen FM. Rigidity of various fixation methods used as dental splints. Dent Traumatol. 1992;8:113–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
7. Andreasen FM, Pedersen BV. Prognosis of luxated permanent teeth –the development of pulp necrosis. Dent Traumatol. 1985;1:207–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
8. Robertson A, Andreasen FM, Andreasen JO, Norén JG. Long-term prognosis of crown-fractured permanent incisors. The effect of stage of root development and associated luxation injury. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2000;10:191–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
9. Wang C, Qin M, Guan Y. Analysis of pulp prognosis in 603 permanent teeth with uncomplicated crown fracture with or without luxation. Dent Traumatol. 2014;30:333–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
10. Finucane D, Kinirons MJ. External inflammatory and replacement resorption of luxated, and avulsed replanted permanent incisors: a review and case presentation. Dent Traumatol. 2003;19:170–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]